What is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition affecting millions of Americans annually and can have significant adverse effects on your health.
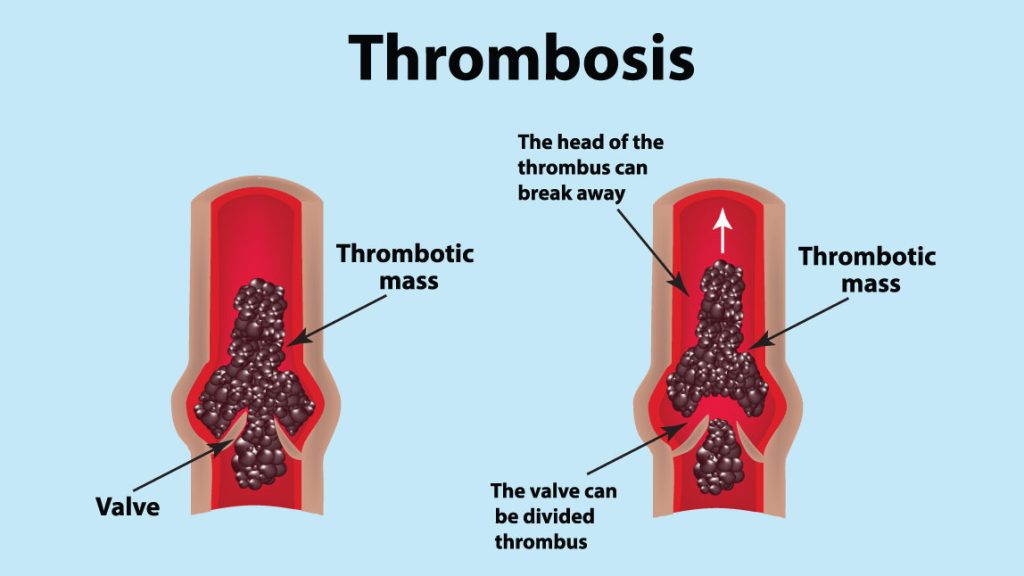
DVT occurs when blood clots form within the deep veins, typically found within the leg muscles. These deep veins are surrounded by leg muscles and are located downstream from a large central vein in the abdomen responsible for returning blood flow to the heart and lungs for oxygenation. The direct path from the legs to the heart and lungs makes DVT particularly risky, as it can impact both leg symptoms and critical heart and lung functions.

Causes of Deep Vein Thrombosis
DVT can arise from various medical and physical factors, including:
Blood Flow Stagnation (stasis)
- This can be caused by prolonged periods of inactivity, such as during long plane rides or hospitalization.
- Inactivity decreases the muscle pump activity in your leg muscles, which causes stagnant blood to become clots.
- Inactivity resulting in DVP is more prevalent in elderly people.
Trauma to the Veins
- If a vein is injured in any way, the body responds to form clots to prevent bleeding.
- While this is important if there is an open bleed, the same process can work too well and cause further problems with excessive clotting.
Increased Blood Thickness (hypercoagulable state)
- Family history of blood clots
- Autoimmune diseases, cancer, or infections can increase inflammation in the body, which can thicken blood
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy or from birth control
- COVID-19 infection has been associated with some serious clotting side effects
- Obesity and tobacco use are also risk factors


Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Symptoms of blood clots in the legs range from asymptomatic to severe. If the clot is on the smaller side, you may not feel anything and often these clots are found during a medical test for another issue.
With larger clots, you have leg swelling, pain, and discoloration. The most concerning complication of DVT is pulmonary embolism (PE), where a clot breaks off and travels to the lungs, causing chest pain and/or shortness of breath. Large PEs can restrict blood flow to the heart and require emergency treatment to prevent death.
Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Treatment by the team at Fox Valley Surgical Specialists typically involves medication to thin the blood and prevent clots from growing any further. This can often be all the treatment required with smaller clots. In cases of extensive DVT or severe symptoms, additional treatments may be necessary.
These can include physically breaking and suctioning out clots or dripping lysing medications (medications that break down cells) into the veins to dissolve the clots. Often, a combination of techniques is needed to achieve effective results.
Have questions or concerns? Please contact Fox Valley Surgical Specialists to help treat venous disease and Deep Vein Thrombosis.
Further Reading: Why are My Veins Blue?








